
Newsroom
A research team led by Prof. WANG Huanqin from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has proposed a semi-supervised medical image segmentation method.
Their work, recently published in Pattern Recognition, addresses the challenge of accurately locating boundaries in semi-supervised medical image segmentation.
Pixel-level annotation of 3D medical images is time-consuming and labor-intensive. To reduce this burden, semi-supervised medical image segmentation has gained attention by using a small set of labeled images along with many unlabeled ones. Most existing techniques rely on consistency regularization and pseudo-labeling to stabilize predictions against data perturbations, thereby improving model generalization. However, these methods can struggle to balance global structural features with fine boundary details.
To overcome this limitation, Prof. WANG's team introduced a novel boundary feature alignment method. This approach aims to learn unified boundary feature representations from both labeled and unlabeled images. A key innovation is the design of a 3D boundary extractor capable of reliably capturing both ground truth and pseudo-label boundaries.
By mixing these boundary types, the model achieves early embedding of boundary features, thereby promoting better alignment and generalization across different annotation states.
Implemented within a standard mean teacher framework, the method was evaluated on three benchmark datasets—LA (left atrium), Pancreas-CT (pancreas), and ACDC (right ventricle, left ventricle, and myocardium). Experimental results show that the proposed approach achieves competitive performance.
Remarkably, on the ACDC dataset with only 10% labeled data, the method outperformed even fully supervised models in key metrics such as 95% Hausdorff Distance and Average Surface Distance.
These results offer a promising direction for reducing the annotation workload in large-scale clinical applications.
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the Anhui Provincial Major Science and Technology Project, and the Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, etc.
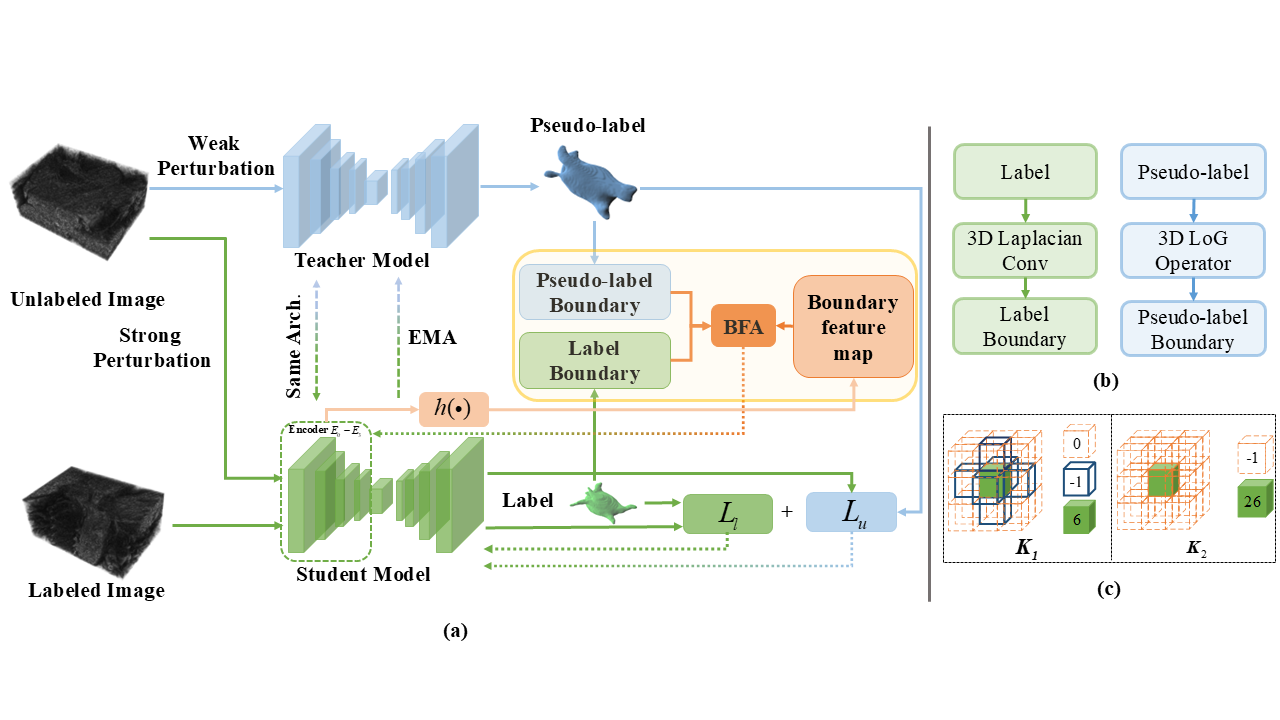
Structure diagram of the semi-supervised learning method for 3D medical image segmentation (Image by GUO Zheng)
